상세 컨텐츠
본문
작성자: 13기 김현지
StyleCLIP 구현하기!
Reference:
- StyleCLIP 논문: StyleCLIP: Text-Driven Manipulation of StyleGAN Imagery
- 동빈나 - 딥러닝 기반의 이미지 편집 기술: StyleCLIP 설명 및 코드 실습
- 동빈나 - StyleCLIP Tutorial
오늘 스터디 목표: 아래 포스팅도 함께 참고하여, Pytorch로 구현된 딥러닝 모델 구조를 이해해보고, github에 있는 딥러닝 모델 오픈소스를 활용하기 위한 간단한 테크닉들을 익혀보자!
[알쓸쿠잡] class 클래스
작성자: 13기 김현지 파이썬 class 개념 정리! Reference: 파이썬 코딩 도장 Unit 34, 파이썬 코딩 도장 Unit 36 Contents 클래스 사용하기 클래스 상속 사용하기 1. 클래스 사용하기 클래스와 메서드 만들
kubig-2021-2.tistory.com
[알쓸쿠잡] PyTorch 사용법1 - 기본&데이터셋
작성자: 13기 김현지 PyTorh 사용법 정리! Reference: PyTorch로 시작하는 딥러닝 입문, 파이토치 한국 사용자 모임-튜토리얼 Contents 파이토치 패키지의 기본 구성 DATASET과 DATALOADER 파이토치 패키지의
kubig-2021-2.tistory.com
[알쓸쿠잡] Pytorch 사용법2 - 신경망 모델 구성 및 사용하기
작성자: 13기 김현지 Pytorch로 신경망 모델 정의하고 사용하기 Reference: 파이토치 사용자 모임-튜토리얼 anweh 티스토리: https://anweh.tistory.com/21?category=946891, https://anweh.tistory.com/22?cate..
kubig-2021-2.tistory.com
StyleCLIP이란?
텍스트 명령어를 이용해 이미지를 원하는 방식으로 수정할 수 있는 모델이다.

Background: StyleGAN (CVPR 2019)
고해상도 이미지를 생성하기 위한 효율적인 아키텍처
Image Manipulation Using StyleGAN

1. Encoding step
: 주어진 이미지 x로부터 그와 매칭되는 적절한 latent vector인 w를 찾는다.
- 어떻게 이미지 x를 latent space에 인코딩할 수 있을까? → 가장 간단한 방법은 Gradient Descent!

latent vector w는 GAN 네트워크에 forwarding 됨으로써 특정한 이미지를 만들어낼 수 있다. 이렇게 만들어진 이미지와 원본 이미지 x 사이에서 similarity를 계산한다. 이렇게 계산된 similarity loss를 이용해서 backporpagation을 진행하고 gradient를 구해서 latent vector를 업데이트하는 방식을 반복한다.
- 어떻게 이미지 x를 latent space에 인코딩할 수 있을까? → 두 번째 방법은 Encoder Network를 학습하는 것
1) Latent vector dataset generation

latent vector를 랜덤하게 샘플링해서 아주 많은 양의 latent vectors와 image pair를 먼저 준비한다. 즉, 어떤 latent vector를 넣었을 때 어떤 이미지가 나올 것이다라는 것을 각각 가상으로 묶어서 데이터 셋을 만든 뒤에 이러한 데이터 셋을 이용해서 인코더 네트워크를 학습한다.
2) Training an encoder network

학습을 하는 데 매우 오래 걸리지만, 학습이 된 이후에는 특정한 이미지가 들어왔을 때 그 이미지에 대한 적절한 latent vector를 찾을 수 있다.
2. Maipulation step
- 인코딩된 latent vector를 어떻게 manipulate 할 수 있을까? → 이미지를 조작하는 가장 기본적인 방법 중 하나는 interpolation이다.
Interpolation은 a라는 포인트에서 b라는 포인트까지 서서히 이동을 시켜보는 것이다.

- 인코딩된 latent vector를 어떻게 manipulate 할 수 있을까? → 두 번째 방법은 learned direction이다.
1) Learns a boundary of an attribute (such a gender, age)

GAN의 latent space에서 특정한 attribute에 대한 decision boundary를 학습한다. 위 예시에서는 남자와 여자를 분류하는 decision boundary를 학습하고 있다.
decision boundary를 학습한 이후에는 두 개의 attribute를 가로지르는 하나의 direction vector를 찾는다. 이 direction vector를 따라 주어진 latent vector를 업데이트하여 정해진 attribute를 바꿀 수 있다.
2) Update a latent vector across the boundary

위에서 남성과 여성을 구분하는 classification boundary를 학습했기 때문에 이 boundary를 따라 이동을 하면 특정 이미지를 여자에서 남자로 바꿀 수 있다.
Background: CLIP(Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training)
image encoder와 text encdoer를 jointly train시킨 네트워크
이미지와 텍스트를 같은 space에 인코딩 시킬 수 있다.
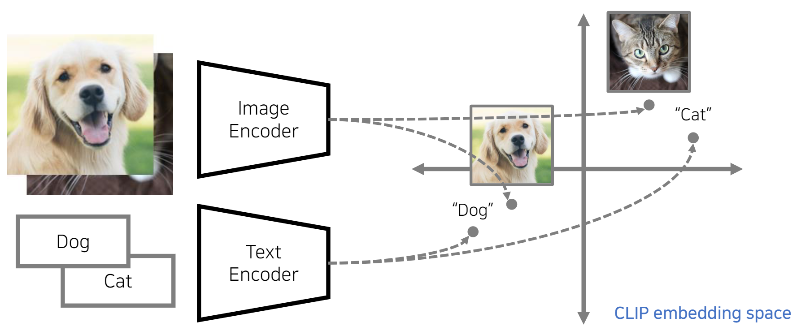
CLIP은 매우 큰 크기의 데이터 셋을 이용해서 두 개의 인코더를 학습했고, 특정한 이미지와 텍스트 사이에서 similarity를 구하기 위해 효과적으로 사용할 수 있다. 즉, 어떤 이미지와 어떤 텍스트가 얼마나 닮아있고, 얼마나 유사한 시멘틱한 의미를 가지고 있는지 판단할 수 있다.
StyleCLIP (StyleGAN + CLIP): Main Idea
어떤 텍스트를 넣었을 때, 그 텍스트에 맞게 이미지를 바꿀 수 있다.
- StyleGAN의 인코딩 과정에서 CLIP loss를 추가한다.
- StyleCLIP은 latent vector w를 업데이트한다.
- latent vector w로부터 만들어진 시멘틱 임베딩 값이 우리가 미리 설정한 텍스트와 유사해질 수 있는 방향으로 latent vector를 업데이트한다.

예를 들어, text를 "without makeup"로 줬을 때, 화장한 이미지가 화장기가 없는 이미지와 유사해지는 방향으로 embedding vector가 업데이트 되도록 latent vector가 optimize된다.
StyleCLIP Method
1. Latent Optimization
Latent optimization: a simple approach for leveraging CLIP to guide image manipulation.

- 오른쪽 term: 특정한 이미지를 임베딩하기 위해 사용
- 왼쪽 term: CLIP Loss
latent vector를 업데이트해서 특정한 인풋 이미지와 유사한 형태를 갖도록 만들면서 그와 동시에 우리가 넣은 텍스트 프롬프트와 유사한 시멘틱 정보를 갖는 이미지를 얻을 수 있는 방향으로 latent vector를 업데이트한다.
2. Latent Mapper
Latent mapper is trained to manipulate the desired attributes of the image as indicated by the text prompt t, while preserving the other visual attributes of the input image.

- 일종의 인코더 네트워크이다.
- Latent Mapper 네트워크는 총 3가지 개별 네트워크로 구분된다. → 각 coarse, middle, fine style로 구분
이와 같은 인코더 네트워크를 학습하는 데는 열 몇 시간 정도 소요될 수 있다. 그러한 한 번 학습이 되고 나면 특정한 이미지에 대해 결과를 한 번의 forward로 얻을 수 있다.
3. Global Directions
Global Direction은 말 그대로 글로벌하게 사용할 수 있는 방향이기 때문에 어떠한 입력이 들어와도 사용할 수 있다.
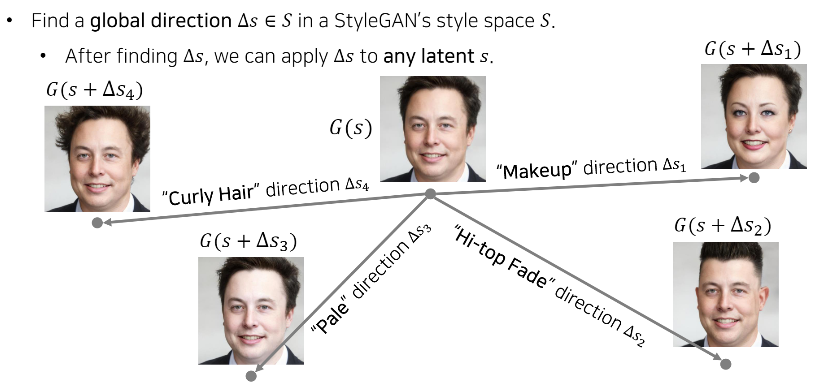
먼저 Curly Hair, Pale, Hi-top Fade, Make up과 같은 다양한 특징에 대한 Global direction을 하나씩 찾은 다음, 특정한 이미지 s가 들어왔을 때, 단순히 s를 그 방향대로 이동한 시키면 원하는 attribute만 바뀐다.
이러한 방향들을 미리 많이 찾아 놓기만 하면 나중에 어떤 이미지가 들어와도 곧바로 그 방향대로 이동시키면 이미지를 변화시킬 수 있다.
StyleCLIP Tutorial 코드 분석
* Colab 환경에서 [런타임 유형]을 GPU로 바꾸고 실행해주세요!
Install CLIP
Github에 있는 CLIP 패키지 설치하기
!pip install ftfy regex tqdm
!pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git- CLIP 패키지 Gihub 저장소
- Github에 있는 패키지 설치하기: pip install git+https://
- *https:// 부터는 패키지가 있는 Github 사이트 url
Load the Pre-trained StyleGAN Model
사전 학습된 StyleGAN 모델 다운 받기
!git clone https://github.com/ndb796/StyleCLIP-Tutorial
%cd StyleCLIP-Tutorial- Github에 있는 오픈소스 내 컴퓨터로 가져오기(Git 저장소 복제하기): git clone [REPO_URL] [DIR]
- [REPO_URL]: 클론해올 저장소의 주소
- [DIR]: 저장소를 로컬에 복제할 위치를 저장. 생략가능하다.
- 사용할 StyleGAN 모델이 있는 Github 저장소
- cd [ 디렉토리 경로]: 이동하려는 디렉토리로 이동
위 코드를 실행하면 아래 Github 저장소를

내 컴퓨터(혹은 Colab 환경)에 복제하여 가져올 수 있다.

모델 가중치 파일 다운로드하기
!wget https://postechackr-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/dongbinna_postech_ac_kr/EVv6yusEt1tFhrL3TCu0Ta4BlpzW3eBMTS0yTPKodNHsNA?download=1 -O stylegan2-ffhq-config-f.pt- 인터넷 상의 파일 다운로드 받기: wget [Download - URL]
- stylegan2-ffhq-config-f.pt: 사전 학습된 StyleGAN2 모델의 가중치
Generator 모델과 사전 학습된 가중치를 불러온 후 모델 초기화시키기
import torch
from stylegan2.model import Generator
g_ema = Generator(1024, 512, 8)
g_ema.load_state_dict(torch.load('stylegan2-ffhq-config-f.pt')["g_ema"], strict=False)
g_ema.eval()
g_ema = g_ema.cuda()- 모델 가중치 저장하고 불러오기: .load_state_dict()
모델 가중치를 불러오기 위해서는, 먼저 모델의 인스턴스(instance)를 생성한 다음에 load_state_dict() 메서드를 사용해서 매개변수들을 불러온다.
- strict=False: 모델의 state_dict의 일부만 불러오거나, 적재하려는 모델보다 더 많은 키를 갖고 있는 state_dict를 불러 올때 설정
- 주로 전이학습을 할 때, 모델의 매개변수 일부만 불러서 사용한다.
- .eval(): 모델을 불러온 후 이 모델을 사용할 경우에 사용한다. (학습할 경우에는 model.train())
학습할 때만 사용하는 개념인 Dropout이나 Batchnorm 등을 비활성화시킨다. 즉, evaluation 과정에서 사용하지 않아야 하는 layer들을 알아서 off 시켜주는 함수이다.
CLIP Loss
CLIP Loss 정의하기
import clip
class CLIPLoss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CLIPLoss, self).__init__()
self.model, self.preprocess = clip.load("ViT-B/32", device="cuda")
self.upsample = torch.nn.Upsample(scale_factor=7)
self.avg_pool = torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=32)
def forward(self, image, text):
image = self.avg_pool(self.upsample(image))
similarity = 1 - self.model(image, text)[0] / 100
return similarity- 참고: 2021.11.24 - [알쓸쿠잡/파이썬] - [알쓸쿠잡] class 클래스, 2021.11.24 - [알쓸쿠잡/프레임워크] - [알쓸쿠잡] Pytorch 사용법2 - 신경망 모델 구성 및 사용하기
- CLIPLoss 클래스는 torch.nn.Module을 상속받는다.
- super().__init__(): super()를 사용해서 기반 클래스(torch.nn.Module)의 메서드를 호출해준다.
- def forward(self, image, text): image와 text를 입력으로 받아 유사도를 계산하고, 그 값을 반환한다.
Latent Optimization
CLIP 네트워크에 포함되어 있는 Text Encoder와 Image Encoder, 그리고 StyleGAN을 이용해서 이미지 manipulation을 진행한다. latent vector w를 업데이트 할 때, latent vector w로 만들어진 이미지 임베딩이 입력한 text prompt와의 similarity가 높아지는 방향으로 업데이트 한다.
mean latent vector를 사용하여 random latent vector 초기화하기
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
mean_latent = g_ema.mean_latent(4096)
latent_code_init_not_trunc = torch.randn(1, 512).cuda()
with torch.no_grad():
img_orig, latent_code_init = g_ema([latent_code_init_not_trunc], return_latents=True,
truncation=0.7, truncation_latent=mean_latent)
# Visualize a random latent vector.
image = ToPILImage()(make_grid(img_orig.detach().cpu(), normalize=True, scale_each=True, range=(-1, 1), padding=0))
h, w = image.size
image.resize((h // 2, w // 2))- 하나의 random latent vector를 만든다.
- mean_latent: latent vector 업데이트 시 기준으로 삼을 평균치를 갖는 latent 생성
- truncation 트릭: 특정한 latent vector가 평균 latent vector로부터 크게 벗어나지 않도록 latent를 잘라내 준다.
- 약 0.7 정도로 설정할 때, 매우 그럴싸한 랜덤 이미지를 만들 수 있다.
- with torch.no_grad(): Pytorch의 autograd engine을 꺼서 메모리 사용량을 줄이고, 연산 속도를 높여준다.
- 우리가 사용하고 있는 사전 학습된 StyleGAN 모델은 1024x1024의 고해상도 이미지를 만들어내기 때문에 너비와 높이를 1/2씩 줄여서 화면에 간단히 출력해본다.
- random vector로 생성하기 때문에 코드를 실행할 때마다 랜덤한 이미지를 얻을 수 있다.
Output:

파라미터 설정하기
from argparse import Namespace
args = Namespace()
args.description = 'A really sad face'
args.lr_rampup = 0.05
args.lr = 0.1
args.step = 150
args.l2_lambda = 0.005 # The weight for similarity to the original image.
args.save_intermediate_image_every = 1
args.results_dir = 'results'
- 가장 중요한 2가지: description과 l2_lambda
- description: 이미지를 manipulation할 때 입력할 text prompt
- l2_lambda: 가중치 파라미터
- 값이 커질수록 원본 이미지와 유사해지려고 한다.
- 값이 작을수록 text prompt와 높은 similarity를 갖게 된다.
latent vector를 최적화시키고, 결과 얻기
import os
import math
import torchvision
from torch import optim
# The learning rate adjustment function.
def get_lr(t, initial_lr, rampdown=0.50, rampup=0.05):
lr_ramp = min(1, (1 - t) / rampdown)
lr_ramp = 0.5 - 0.5 * math.cos(lr_ramp * math.pi)
lr_ramp = lr_ramp * min(1, t / rampup)
return initial_lr * lr_rampThe learning rate adjustment function
- learning rate을 각 스텝마다 적절히 조정해서 적용할 수 있도록 한다.
- 즉, 고정된 특정한 learning rate만 사용하는 것이 아니라 스탭이 반복될 때 learning rate를 적절히 조정해 optimization을 보다 매끄럽게 수행할 수 있도록 한다.
text_inputs = torch.cat([clip.tokenize(args.description)]).cuda()
os.makedirs(args.results_dir, exist_ok=True)- 우리가 입력한 description(args.description)은 먼저 토큰화된 이후에 CLIP 인코더에 들어갈 수 있게 된다.
# Initialize the latent vector to be updated.
latent = latent_code_init.detach().clone()
latent.requires_grad = True
clip_loss = CLIPLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam([latent], lr=args.lr)Initialize the latent vector to be updated
- Adam optimizer를 이용해서 latent vector 업데이트한다.
for i in range(args.step):
# Adjust the learning rate.
t = i / args.step
lr = get_lr(t, args.lr)
optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"] = lr
# Generate an image using the latent vector.
img_gen, _ = g_ema([latent], input_is_latent=True, randomize_noise=False)
# Calculate the loss value.
c_loss = clip_loss(img_gen, text_inputs)
l2_loss = ((latent_code_init - latent) ** 2).sum()
loss = c_loss + args.l2_lambda * l2_loss
# Get gradient and update the latent vector.
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Log the current state.
print(f"lr: {lr}, loss: {loss.item():.4f}")
if args.save_intermediate_image_every > 0 and i % args.save_intermediate_image_every == 0:
with torch.no_grad():
img_gen, _ = g_ema([latent], input_is_latent=True, randomize_noise=False)
torchvision.utils.save_image(img_gen, f"results/{str(i).zfill(5)}.png", normalize=True, range=(-1, 1))
with torch.no_grad():
img_orig, _ = g_ema([latent_code_init], input_is_latent=True, randomize_noise=False)
# Display the initial image and result image.
final_result = torch.cat([img_orig, img_gen])
torchvision.utils.save_image(final_result.detach().cpu(), os.path.join(args.results_dir, "final_result.jpg"), normalize=True, scale_each=True, range=(-1, 1))- 각각의 스탭마다 위 코드가 반복적으로 수행된다.
- 먼저 learning rate를 조정한 뒤에 latent vector를 이용해서 이미지를 생성한다.
- 생성한 이미지와 우리가 입력한 text prompt가 높은 similarity를 갖도록 업데이트 해준다.
- 그와 동시에 초기 latent vector와도 유사하도록, 즉 원본 이미지를 유지하도록 latent vactor를 제한하는 l2_loss를 넣어준다.
- 이 두 가지 loss를 이용해 latent vector를 optimization한다.
- 이 loss를 기반으로 역전파를 수행한 뒤에 그레디언트를 구해선 latent vector를 업데이트 한다.
- 구글 Colab환경에서 약 2~3분 정도 소요된다.
Result Visualization
result_image = ToPILImage()(make_grid(final_result.detach().cpu(), normalize=True, scale_each=True, range=(-1, 1), padding=0))
h, w = result_image.size
result_image.resize((h // 2, w // 2))- 왼쪽: 원본 이미지, 오른쪽: 최종 결과 이미지
- text prompt로 'A really sad face'을 넣은 결과 원본 이미지를 슬픈 표정의 이미지로 변화시켰다.
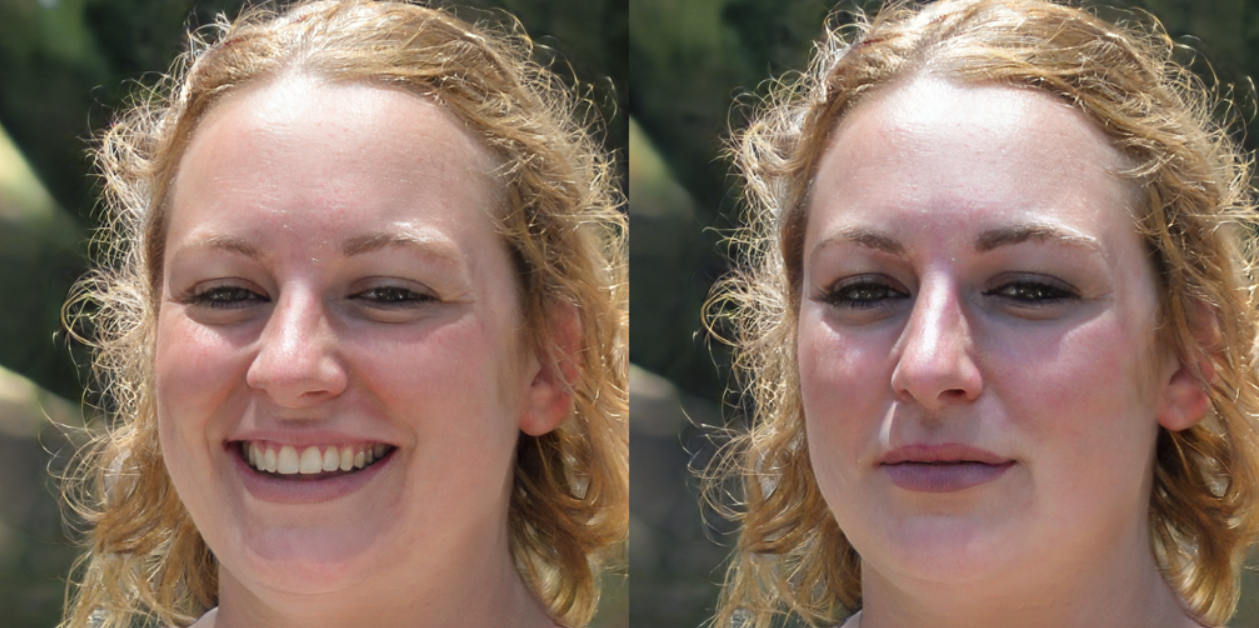
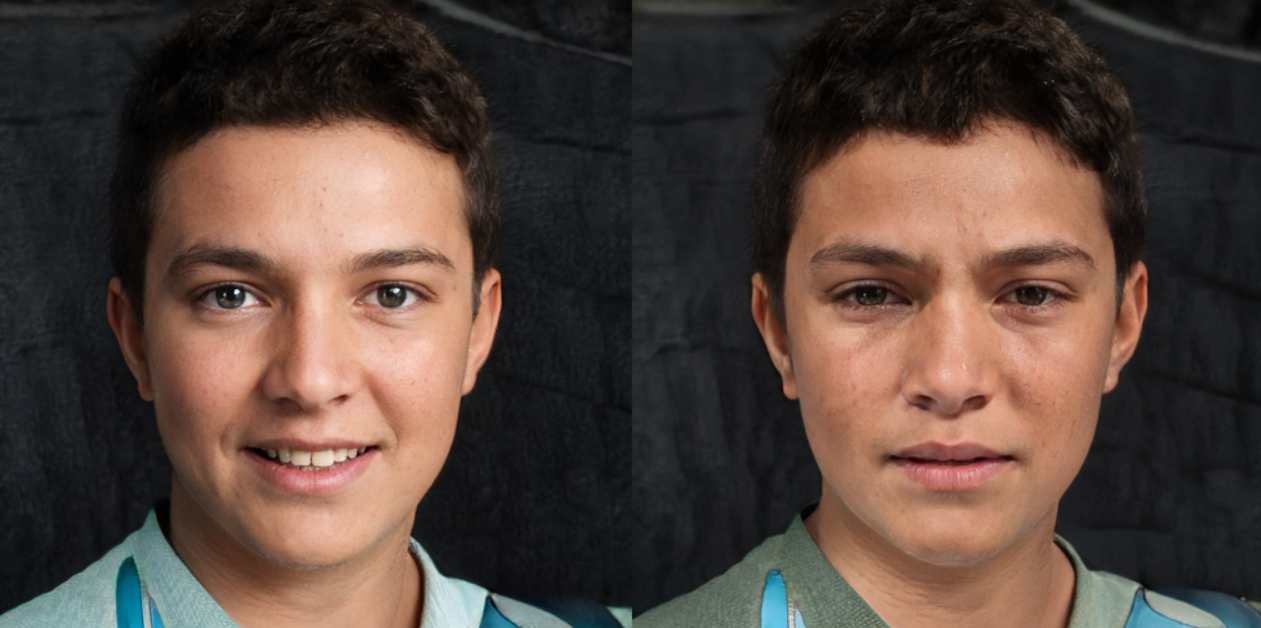


- 이미지가 서서히 변화하는 과정을 담은 몰핀 비디오 또한 다운받을 수 있다. 총 150번의 스탭을 반복했기 때문에 150프레임으로 구성된 동영상을 생성하여 다운로드 할 수 있다.
!ffmpeg -r 15 -i results/%05d.png -c:v libx264 -vf fps=25 -pix_fmt yuv420p out.mp4
from google.colab import files
files.download('out.mp4')'심화 스터디 > 코드 분석 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [코드 분석 스터디] Top 100 Korean Dramas (0) | 2021.11.23 |
|---|---|
| [코드 분석 스터디] Spooky Author Prediction_NLP tutorial (0) | 2021.11.14 |
| [코드 분석 스터디] Natural Language Processing : Bag of Words for IMDB movie review (0) | 2021.11.13 |
| [코드 분석 스터디] Segmentation : Sementic Segmentation - CARLA Image Road segmentation (1) | 2021.11.04 |
| [코드 분석 스터디] Time Series Regression - Predict Future Sales 커널 필사 (2) | 2021.10.01 |




댓글 영역